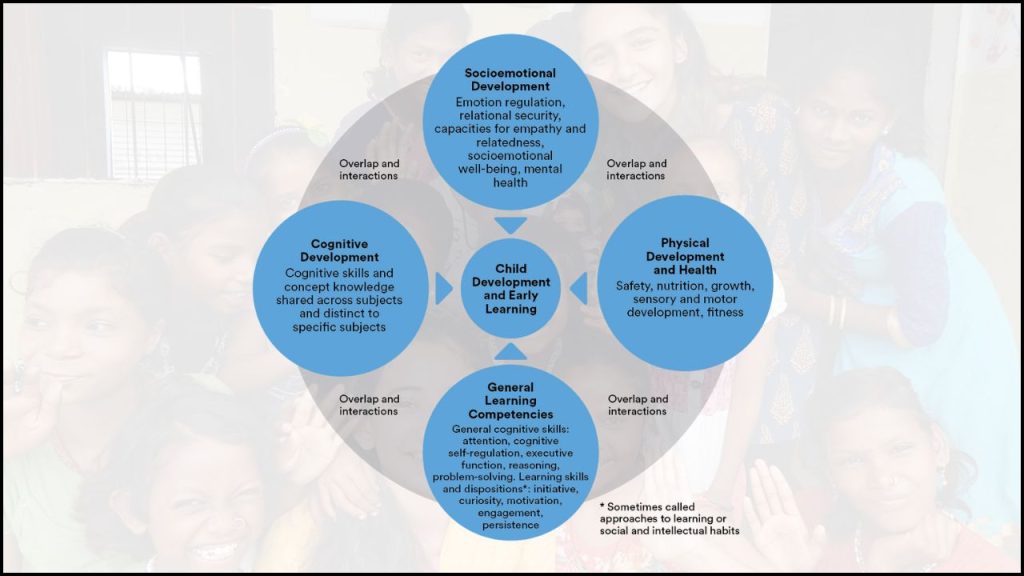
A strong focus on child development and psychology ensures that children grow in a supportive and understanding environment. Teachers who understand developmental stages and psychological needs of children can provide better guidance and foster emotional, social, and academic growth. Early childhood experiences form the foundation for lifelong learning and behavior.
Table of Contents
Understanding Child Psychology
Child psychology explains how children think, feel, and behave at different ages. This knowledge helps educators respond to children’s needs effectively.
- Cognitive growth happens in stages.
- Emotional well-being affects learning and behavior.
- Social development is key for communication and teamwork.
- Individual differences in behavior must be respected.
Important Concepts in Child Psychology
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Attachment Theory | Children form emotional bonds with caregivers that affect their future trust. |
| Behavioral Theories | Actions are shaped by rewards, punishments, and the environment. |
| Cognitive Development | Thinking ability changes with age and experience. |
| Social Learning | Children learn through observation and imitation. |
Developmental Stages of Children
Children pass through different stages, and each stage requires specific educational strategies.
Key Developmental Stages
| Stage | Age Range | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Infancy | 0–2 years | Rapid brain development, sensory exploration, and bonding with adults |
| Toddlerhood | 2–3 years | Language starts, basic motor skills, and simple decision-making |
| Preschool Age | 3–5 years | Imagination, emotional expression, start of social interaction |
| Early School Age | 6–8 years | Reading, basic math, teamwork, and following rules |
| Middle Childhood | 9–11 years | Logical thinking, emotional self-control, and growing independence |
Classroom Applications Based on Developmental Understanding
Teaching methods must match children’s age and stage to be effective.
- Hands-on activities suit younger children.
- Group tasks promote teamwork in middle childhood.
- Visual aids help with concept building.
- Stories and role play make learning relatable.
Stage-wise Teaching Strategies
| Age Group | Teaching Focus |
|---|---|
| 3–5 years | Use of colorful materials, storytelling, and simple games |
| 6–8 years | Basic academic skills, group play, and routine building |
| 9–11 years | Critical thinking, project-based learning, peer collaboration |
Role of Emotions in Learning
Emotions strongly impact a child’s ability to learn.
- Positive emotions encourage creativity and curiosity.
- Fear or anxiety can block learning.
- Trust in teachers builds a safe learning space.
- Praise and encouragement boost confidence.
Emotional Needs of Children
| Need | Impact on Learning |
|---|---|
| Love and Affection | Builds confidence, improves attention |
| Safety and Security | Reduces stress, improves participation |
| Recognition | Encourages effort, motivates improvement |
| Understanding | Promotes trust, eases behavior issues |
Social Development and Peer Interaction
Social skills shape a child’s ability to work and live with others.
- Sharing and taking turns teach cooperation.
- Group activities build friendships and respect.
- Classroom discussions develop expression and listening.
- Conflict resolution lessons improve emotional control.
Important Social Skills in Elementary Education
| Skill | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Communication | Better understanding, reduced conflicts |
| Empathy | Stronger friendships, respectful behavior |
| Cooperation | Group learning, teamwork success |
| Self-Regulation | Better classroom behavior, focus on tasks |
Individual Differences and Inclusive Learning
Every child learns differently. Teachers must understand these differences.
- Learning pace varies from child to child.
- Multiple intelligences include music, logic, body movement, and language.
- Special needs require personalized support.
- Cultural background influences behavior and learning style.
Inclusive Teaching Techniques
| Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Flexible instruction | Adapts to various learning speeds |
| Visual and audio tools | Supports children with different learning styles |
| Peer mentoring | Encourages social and academic support |
| Assistive technologies | Helps children with disabilities access learning materials |
Importance of Play in Child Development
Play is not just fun—it is a vital educational tool.
- Motor skills improve through physical play.
- Social play teaches rules and interaction.
- Pretend play builds imagination and problem-solving.
- Games with rules teach patience and strategy.
Types of Play and Their Benefits
| Type of Play | Development Area |
|---|---|
| Physical play | Strength, coordination, and energy release |
| Constructive play | Creativity, logic, and planning |
| Fantasy play | Imagination, emotional expression |
| Cooperative play | Teamwork, leadership, and social bonding |
Teacher’s Role in Child Development
Teachers influence not only academics but also emotional and social development.
- Observing behavior helps identify needs early.
- Guiding with empathy encourages positive growth.
- Collaborating with parents strengthens support.
- Creating a secure environment promotes better learning.
Qualities of an Effective Elementary Educator
| Quality | Effect on Children |
|---|---|
| Patience | Allows every child to progress at their pace |
| Sensitivity | Builds emotional safety and trust |
| Creativity | Makes lessons engaging and effective |
| Consistency | Establishes discipline and structure |
Summing Up
Understanding child psychology and developmental stages is crucial in elementary education. Children need more than just textbooks—they need attention, understanding, and proper emotional support. When teachers apply psychological knowledge and adapt their methods, every child gets a fair chance to succeed. A development-focused approach builds not only knowledge but also strong, happy individuals.





